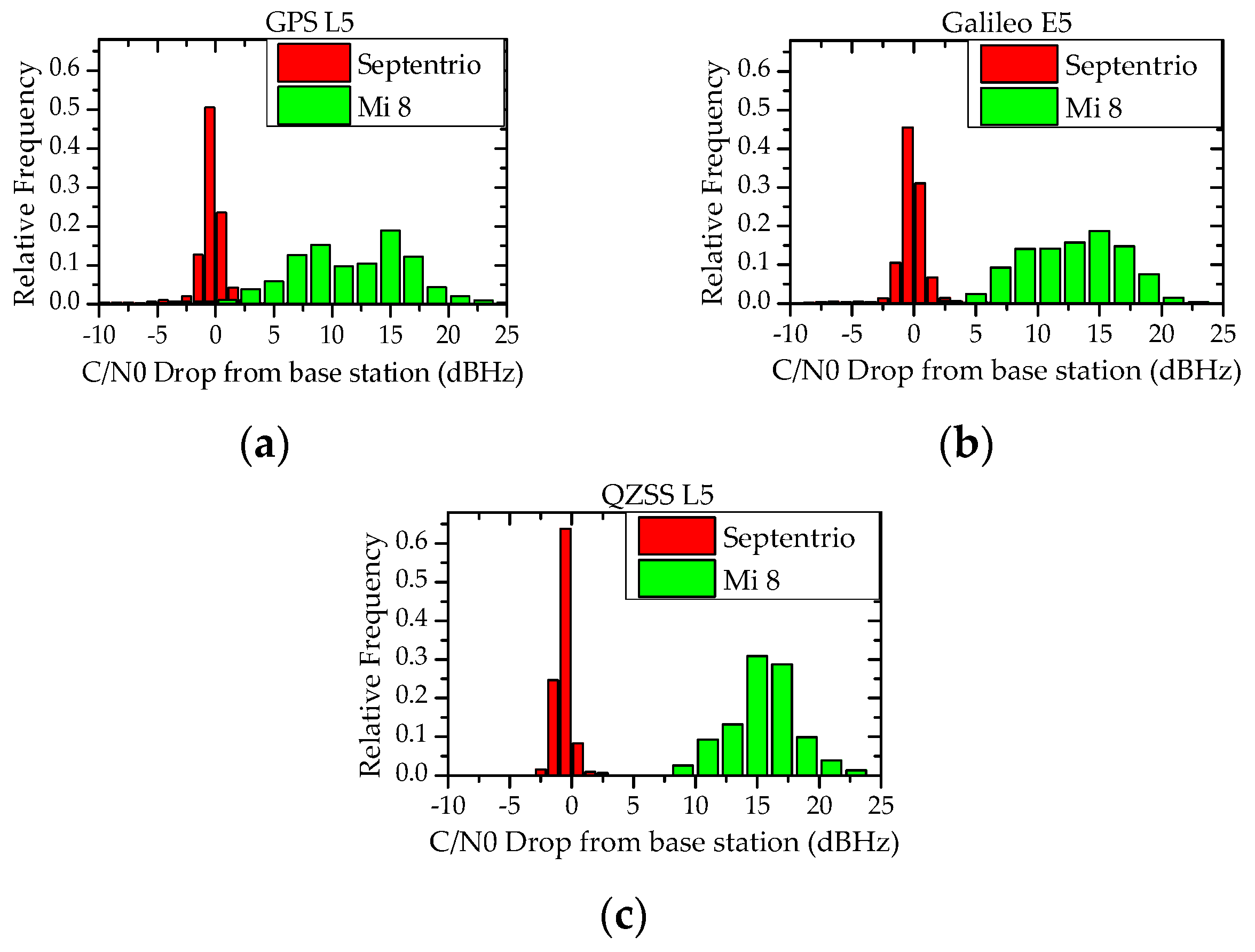
The carrier to noise ratio is defined as the ratio of the received modulated carrier signal power c to the received noise power n after the receiver filters.
Dropped noise floor at carrier frequency.
In signal theory the noise floor is the measure of the signal created from the sum of all the noise sources and unwanted signals within a measurement system where noise is defined as any signal other than the one being monitored.
The noise floor can be defined as the measure of the signal created from the sum of all the noise sources and unwanted signals within a system.
If the carrier is considered as dc the frequencies measured with respect to the carrier are referred to as baseband offset from the carrier modulation noise or fourier frequencies.
Modulation related frequencies are designated f.
The noise power in the receiver intermediate frequency if filter bandwidth that comes from ktb.
High frequency noise while computers and other electronic equipment generate noise in all frequency ranges.
The voltage adds to the.
However some references take the mds to be 3 or more db higher than the receiver noise floor.
Place the spectrum analyzer in video averaging mode and get the noise floor average across frequency or danl in db.
This data clearly shows that the medium frequency am band is significantly more affected by the noise floor than the vhf uhf or mobile cellphone service bands.
This is related to the spectrum analyzer s noise figure and is a measure of the sensitivity of the analyzer.
For this reason the term minimum discernable signal mds is often used interchangeably with noise floor.
Letter 1 represents frequency for carrier related measures.
For the signal to be detected it must be higher than the noise floor 6.
The level of the noise floor determines the lowest strength signals that can be received and therefore the noise floor level is an important characteristic of any radio.
A reduction of 9 11 db in the noise floor level is realized between the city and rural environments over the 300 khz to 100mhz band.
The system designer usually specifies a carrier to noise ratio.
The 150 mv dropped across rl in the bottom ground return line arises from the 30 ma of current flowing in 5 2 w of lead wire resistance.
At this point we would like to know the noise floor in our receiver i e.
Since the units of ktb are watts hz calculate the noise floor in the channel bandwidth by multiplying the noise power in a 1 hz bandwidth by the overall equivalent noise.
When both carrier and noise are measured across the same impedance this ratio can equivalently be given as.
Building a completely noise.
In radio communication and electronics this may include thermal noise black body cosmic noise as well as atmospheric noise from distant thunderstorms and.